前言
基本上每一种编程语言都会支持多线程,这里我们只讲C/C++,C/C++是真正的native language。
现代操作系统都是支持多线程的,不管是单核还是多核,多线程的编程,也可以非常有效的利用CPU的执行来解决很多复杂的问题,并且在多核的情况下更好的让多核CPU核心共同协调工作。
- Posix Threads(pthread): 对不同platform的支持很好,你可以非常稳定可靠的使用,如果想让你的代码可移植性非常强的话,使用
pthread是毫无疑问的
- std::thread: 是从C++11中引入,在不同的平台上表现各异,比如在一些Android和Win64平台下不支持,或者有性能瓶颈,当然了如果你的代码只是考虑到Linux/gcc平台编译器的话,是个不错的选择,特别是对C++11的类非常友好
- boost::thread: 对
std::thread是个非常好的替代品,而且API也非常相似,但是boost::thread是一个第三方库,一般都需要移植到你正在使用的平台
但是总的来说还是要以发展的眼光看待std::thread,毕竟C++的所谓现代化API也一直在更新发展,不知道后面是会主打兼容性还是高性能,还有可能会两者兼顾。
这里,还是采用基于Posix Threads来写一个线程管理的工具类,通常也可以认为是一个线程池。
设计思想
设计一个ThreadManager类,来给别的代码使用,提供如下API
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| static Result ThreadManager::create(ThreadManager** ppInstance, const char* pName);
void destroy();
Result registerJobFamily(JobFunc jobFuncAddr, const char* pJobFuncName, JobHandle* phJob);
Result unregisterJobFamily(JobFunc jobFuncAddr, const char* pJobFuncName, JobHandle* phJob);
Result postJob(JobHandle hJob, void* pData, uint64_t requestId);
Result removeJob(JobHandle hJob, void* pData);
Result getAllPostedJobs(JobHandle hJob, std::vector<void*>& rPostedJobs);
Result flushJob(JobHandle hJob, bool forceFlush);
bool isJobAvailable(JobHandle hJob);
|
看了这些API大致了解到这个类是如何使用的了,也没有过多复杂的接口,可以看到这里使用JobHandle来作为一个任务的唯一标识。
1
| typedef uint64 JobHandle;
|
后面会看到一些内部使用的数据结构,很容易明白是如何设计的。
作为一个线程池的工具类,主要的目的是在需要运行自己的工作线程之前,把线程的资源都分配好,可以更快的让线程运行起来,并且对该线程池的资源的管理和使用。
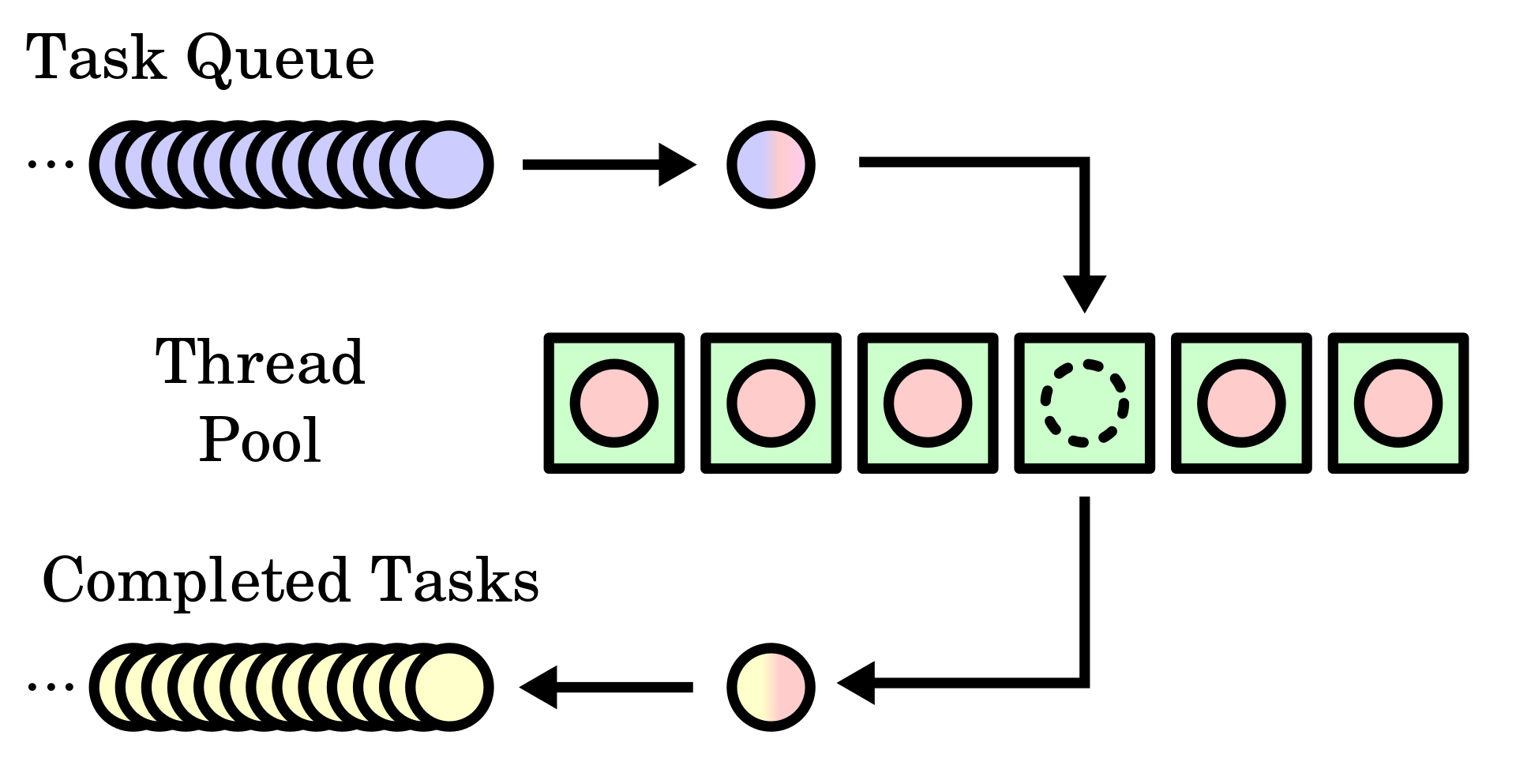
每一个JobHandle都可以插入多个任务组成一个PendingQueue,依次执行,也可以设计优先级去处理,这里的代码没有设计优先级,实行先进先出(FIFO)的规则。
设计一个线程管理或者说线程池,其实难度在于如何处理多线程带来的资源保护和线程状态切换,以及如何保证性能不受影响。
码代码
首先还是来看数据结构,数据结构基本决定了代码都走向和设计风格,以及写代码的人到底在想些什么,考虑到了哪些部分等。
注册线程Job的信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| struct RegisteredJob {
JobFunc funcAddr;
char name[MaxNameLength];
bool isUsed;
uint64_t hRegister;
uint32_t slot;
uint32_t uniqueCounter;
OSThreadHandle hRegisteredThread;
JobFlushStatus flushStatus;
};
typedef void* (*JobFunc)(void* pArg);
typedef pthread_t OSThreadHandle;
static const JobFlushStatus Noflush = 0;
static const JobFlushStatus FlushRequested = 1;
static const JobFlushStatus Flushed = 2;
|
- funcAddr: 是注册的Job的工作函数
- name: 是注册的Job的名称
- isUsed: 该Job是否已经被使用
- hRegister: 注册的Job的handle值,通过slot和count组合而成
- slot: 注册的Job的slot
- uniqueCounter: 注册的Job的id号
- hRegisteredThread: 注册的线程的句柄
- flushStatus: flush的状态值
Job的Runtime信息,每一个等待或者正在执行的Job都具有一个RutimeJob结构体对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| struct RuntimeJob {
uint64_t hJob;
void* pData;
uint64_t requestId;
JobStatus status;
};
enum class JobStatus {
Submitted,
Ready,
OnHold,
Stopped,
Invalid,
};
|
- hJob: Job的handle唯一标识
- pData: 工作函数携带的私有数据
- requestId: 请求id号,可以通过requestId号来重排PendingQueue中任务的优先级
- status: 工作状态
线程的控制参数,保护线程信息和RuntimeJob中的一些状态和线程的控制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| struct ThreadControl {
NativeMutex* pThreadLock;
NativeMutex* pFlushJobSubmitLock;
NativeMutex* pQueueLock;
NativeMutex* pFlushLock;
NativeCondition* pReadOK;
NativeCondition* pFlushOK;
CoreStatus status;
volatile bool jobPending;
volatile uint32_t blockingStatus;
bool isAvailable;
};
static const CoreStatus Error = 0;
static const CoreStatus Initialized = 1;
static const CoreStatus Stopped = 2;
|
- pThreadLock: 确保线程依次运行,不被抢占
- pFlushJobSubmitLock: 保护flashStatus
- pQueueLock: 保护PendingQueue数据
- pFlushLock: 保护flash状态
- pReadOK: 等待线程被触发信号
- pFlushOK: 等待线程被释放信号
- status: 线程的状态值
- jobPending: 任务队列是否空闲
- blockingStatus: 确保线程释放完成
- isAvailable: 线程是否空闲
线程配置信息结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| struct ThreadData {
std::deque<RuntimeJob*> pq;
};
struct ThreadConfig {
uint32_t threadId;
OSThreadHandle hWorkThread;
JobFunc workThreadFunc;
void* pContext;
ThreadData data;
ThreadControl ctrl;
bool isUsed;
};
|
- threadId: 线程ID号
- hWorkThread: 线程句柄
- workThreadFunc: 线程回调函数
- pContext: 上下文句柄,通常为ThreadManager指针
- data: 挂载在该线程上的等待队列
- ctrl: 线程控制类
- isUsed: 该线程是否被使用
类的成员变量
1
2
3
4
5
| char m_name[MaxNameLength];
uint32_t m_totalNumOfRegisteredJob;
RegisteredJob m_registeredJobs[MaxRegisteredJobs];
ThreadConfig m_threadWorker[MaxNumThread];
NativeMutex* m_pRegisteredJobLock;
|
创建/销毁ThreadManager对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| Result ThreadManager::create(ThreadManager** ppInstance, const char* pName)
{
Result result = -EFailed;
ThreadManager* pLocalInstance = NULL;
pLocalInstance = new ThreadManager();
if(NULL != pLocalInstance) {
result = pLocalInstance->initialize(pName);
if(Ok != result) {
delete pLocalInstance;
pLocalInstance = NULL;
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to create threadmanager" << endl;
}
}
if(Ok == result) {
*ppInstance = pLocalInstance;
}
return result;
}
Result ThreadManager::initialize(const char* pName)
{
Result result = Ok;
if(NULL == pName) {
pName = "ThreadManager";
}
::strncpy(m_name, pName, sizeof(m_name));
m_pRegisteredJobLock = NativeMutex::create();
if(NULL == m_pRegisteredJobLock) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to initialize " << pName << endl;
result = -EFailed;
} else {
::memset(&m_registeredJobs, 0x00, sizeof(m_registeredJobs));
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < MaxNumThread; i++) {
m_threadWorker[i].threadId = 0;
m_threadWorker[i].workThreadFunc = NULL;
m_threadWorker[i].pContext = NULL;
::memset(&m_threadWorker[i].ctrl, 0x00, sizeof(ThreadControl));
m_threadWorker[i].isUsed = false;
}
}
return result;
}
ThreadManager::~ThreadManager()
{
Result result = Ok;
if(m_totalNumOfRegisteredJob > 0) {
RegisteredJob* pRegisteredJob = NULL;
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < MaxRegisteredJobs; i++) {
pRegisteredJob = &m_registeredJobs[i];
if(0 != pRegisteredJob->hRegister) {
result = unregisterJobFamily(NULL, pRegisteredJob->name,
pRegisteredJob->hRegister);
if(Ok != result) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to process unregisterJobFamily slot " <<
pRegisteredJob->slot << endl;
}
}
}
}
m_pRegisteredJobLock->destroy();
m_pRegisteredJobLock = NULL;
}
|
注册线程过程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
| Result ThreadManager::registerJobFamily(JobFunc jobFuncAddr, const char* pJobFuncName,
JobHandle* phJob)
{
Result result = Ok;
uint32_t slot = 0;
uint32_t count = 0;
RegisteredJob* pRegisteredJob = NULL;
bool jobAlreadyRegistered = isJobAlreadyRegistered(phJob);
bool freeSlotsAvailable = isFreeSlotAvailable(&slot, &count);
if((true == jobAlreadyRegistered) ||
(false == freeSlotsAvailable))
{
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to registerJobFamily, jobAlreadyRegistered: " <<
jobAlreadyRegistered << ", freeSlotsAvailable: " <<
freeSlotsAvailable << endl;
result = -EFailed;
}
if(Ok == result) {
pRegisteredJob = &m_registeredJobs[slot];
::memset(pRegisteredJob, 0x00, sizeof(RegisteredJob));
pRegisteredJob->funcAddr = jobFuncAddr;
pRegisteredJob->slot = slot;
pRegisteredJob->uniqueCounter = count;
pRegisteredJob->isUsed = true;
::strncpy(pRegisteredJob->name, pJobFuncName, MaxNameLength);
*phJob = packJobHandleFromRegisteredJob(pRegisteredJob);
pRegisteredJob->hRegister = *phJob;
result = startThreads(slot, phJob);
if(Ok == result) {
if(0 != pRegisteredJob->hRegisteredThread) {
setFlushStatus(*phJob, Noflush);
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to get thread handle" << endl;
result = -EFailed;
}
}
}
return result;
}
JobHandle packJobHandleFromRegisteredJob(RegisteredJob* pRegisteredJob)
{
JobHandle handle = InvalidJobHandle;
handle = pRegisteredJob->uniqueCounter;
handle = handle << 32;
handle |= pRegisteredJob->slot;
return handle;
}
Result ThreadManager::startThreads(uint32_t slot, JobHandle* phJob)
{
RegisteredJob* pRegisteredJob = getJobByHandle(*phJob);
Result result = Ok;
ThreadConfig* pCfg = NULL;
pCfg = &m_threadWorker[slot];
if((NULL == pRegisteredJob) || (pCfg->isUsed == true)) {
result = -EFailed;
} else {
pCfg->threadId = pRegisteredJob->uniqueCounter;
pCfg->workThreadFunc = workerThreadBody;
pCfg->ctrl.pReadOK = NativeCondition::create();
pCfg->ctrl.pThreadLock = NativeMutex::create();
pCfg->ctrl.pFlushJobSubmitLock = NativeMutex::create();
pCfg->ctrl.pQueueLock = NativeMutex::create();
pCfg->ctrl.pFlushOK = NativeCondition::create();
pCfg->ctrl.pFlushLock = NativeMutex::create();
pCfg->ctrl.isAvailable = true;
pCfg->pContext = reinterpret_cast<void*>(this);
pCfg->isUsed = true;
if((NULL == pCfg->ctrl.pReadOK) ||
(NULL == pCfg->ctrl.pThreadLock) ||
(NULL == pCfg->ctrl.pFlushJobSubmitLock) ||
(NULL == pCfg->ctrl.pQueueLock))
{
LOG(ERROR) << "Couldn't read lock resource. slot " << slot <<
" m_totalNumOfRegisteredJob " << m_totalNumOfRegisteredJob << endl;
pCfg->isUsed = false;
result = -EFailed;
}
if(Ok == result) {
result = OsUtils::threadCreate(pCfg->workThreadFunc,
pCfg, &pCfg->hWorkThread);
if(Ok == result) {
pRegisteredJob->hRegisteredThread = pCfg->hWorkThread;
pCfg->ctrl.pThreadLock->lock();
setStatus(&pCfg->ctrl, Initialized);
pCfg->ctrl.pThreadLock->unlock();
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Couldn't create worker thread, logical threadId " <<
pCfg->threadId << endl;
pCfg->isUsed = false;
result = -EFailed;
}
}
}
return result;
}
void* ThreadManager::workerThreadBody(void* pArg)
{
ThreadConfig* pConfig = NULL;
pConfig = reinterpret_cast<ThreadConfig*>(pArg);
if(NULL != pConfig) {
ThreadManager* pThreadManager = reinterpret_cast<ThreadManager*>(pConfig->pContext);
pThreadManager->doWork(pArg);
}
return NULL;
}
void* ThreadManager::doWork(void* pArg)
{
Result result = Ok;
ThreadConfig* pConfig = NULL;
ThreadControl* pCtrl = NULL;
pConfig = reinterpret_cast<ThreadConfig*>(pArg);
pCtrl = &pConfig->ctrl;
if(NULL == pCtrl) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to start" << endl;
} else {
pCtrl->pThreadLock->lock();
while(Stopped != getStatus(pCtrl)) {
while((Stopped != getStatus(pCtrl)) && (false == pCtrl->jobPending)) {
pCtrl->pReadOK->wait(pCtrl->pThreadLock->getNativeHandle());
}
if(Stopped != getStatus(pCtrl)) {
pCtrl->jobPending = false;
pCtrl->pThreadLock->unlock();
}
result = processJobQueue(pConfig);
if(true == getFlushBlockStatus(pCtrl)) {
pCtrl->pFlushLock->lock();
setFlushBlockStatus(pCtrl, false);
pCtrl->pFlushOK->signal();
pCtrl->pFlushLock->unlock();
}
pCtrl->pThreadLock->lock();
if(Ok != result) {
LOG(ERROR) << "ProcessJobQueue failed with result" << endl;
}
}
pCtrl->pThreadLock->unlock();
}
return NULL;
}
|
发送任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
| Result ThreadManager::postJob(JobHandle hJob, void* pData, uint64_t requestId)
{
RuntimeJob* pRuntimeJob = NULL;
Result result = Ok;
ThreadControl* pCtrl = NULL;
pCtrl = getThreadControlByHandle(hJob);
if(NULL == pCtrl) {
LOG(ERROR) << "pCtrl is null" << endl;
result = -EFailed;
} else {
if(Initialized != getStatus(pCtrl)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Thread is not initialized threadId" << endl;
result = -EFailed;
} else {
void* vbuf = malloc(sizeof(RuntimeJob));
::memset(vbuf, 0x00, sizeof(RuntimeJob));
pRuntimeJob = reinterpret_cast<RuntimeJob*>(vbuf);
if(NULL != pRuntimeJob) {
pRuntimeJob->hJob = hJob;
pRuntimeJob->requestId = requestId;
pRuntimeJob->pData = pData;
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->lock();
result = addToPriorityQueue(pRuntimeJob);
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->unlock();
if(Ok != result) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Couldn't add job to Priority Queue" << endl;
} else {
result = trigger(hJob);
if(Ok != result) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Filed to trigger" << endl;
}
}
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to create runtimejob out of memory" << endl;
result = -ENoMemory;
}
}
}
if(result == Ok) {
pCtrl->isAvailable = false;
}
return result;
}
Result ThreadManager::trigger(JobHandle hJob)
{
Result result = Ok;
ThreadControl* pCtrl = NULL;
pCtrl = getThreadControlByHandle(hJob);
if(NULL == pCtrl) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to get threadctrl " << pCtrl << endl;
result = -EFailed;
} else {
pCtrl->pThreadLock->lock();
pCtrl->jobPending = true;
pCtrl->pThreadLock->unlock();
pCtrl->pReadOK->signal();
}
return result;
}
Result ThreadManager::processJobQueue(void* pCfg)
{
uint32_t result = Ok;
ThreadConfig* pConfig = NULL;
ThreadControl* pCtrl = NULL;
ThreadData* pData = NULL;
RuntimeJob* pJob = NULL;
bool isQueued = false;
pConfig = reinterpret_cast<ThreadConfig*>(pCfg);
pCtrl = &pConfig->ctrl;
pData = &pConfig->data;
pCtrl->pQueueLock->lock();
if(false == pData->pq.empty()) {
isQueued = true;
}
pCtrl->pQueueLock->unlock();
while(true == isQueued) {
pCtrl->pQueueLock->lock();
pJob = pData->pq.front();
if(NULL != pJob) {
switch(pJob->status) {
case JobStatus::Submitted:
if(FlushRequested == getFlushStatus(pJob->hJob)) {
pJob->status = JobStatus::Stopped;
} else if(Noflush == getFlushStatus(pJob->hJob)) {
pJob->status = JobStatus::Ready;
}
break;
case JobStatus::Stopped:
break;
default:
break;
}
pData->pq.pop_front();
pCtrl->pQueueLock->unlock();
if(pJob->status == JobStatus::Ready) {
dispatchJob(pJob);
}
::free(pJob);
pJob = NULL;
}
pCtrl->pQueueLock->lock();
if(true == pData->pq.empty()) {
isQueued = false;
pCtrl->isAvailable = true;
}
pCtrl->pQueueLock->unlock();
}
return result;
}
void ThreadManager::dispatchJob(RuntimeJob* pJob)
{
JobFunc func = getJobFunc(pJob->hJob);
if(NULL != func) {
func(pJob->pData);
}
}
|
移除任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| Result ThreadManager::removeJob(JobHandle hJob, void* pRemoveJobData)
{
Result result = Ok;
ThreadData* pData = NULL;
ThreadControl* pCtrl = NULL;
pData = getThreadDataByHandle(hJob);
pCtrl = getThreadControlByHandle(hJob);
if((NULL == pData) || (NULL == pCtrl)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to get threaddata or threadcontrol" << endl;
result = -EFailed;
} else {
pCtrl->pQueueLock->lock();
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < pData->pq.size(); ++i) {
RuntimeJob* pJob = pData->pq[i];
if(pRemoveJobData == pJob->pData) {
pData->pq.erase(pData->pq.begin() + i);
}
}
pCtrl->pQueueLock->unlock();
}
return result;
}
|
退出线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| Result ThreadManager::flushJob(JobHandle hJob, bool forceFlush)
{
Result result = Ok;
ThreadControl* pCtrl = getThreadControlByHandle(hJob);
if(NULL == pCtrl) {
result = -EFailed;
} else {
if(Initialized != getStatus(pCtrl)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Thread is not initialized" << endl;
result = -EFailed;
} else {
if(Noflush == getFlushStatus(hJob)) {
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->lock();
setFlushStatus(hJob, FlushRequested);
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->unlock();
setFlushBlockStatus(pCtrl, true);
result = trigger(hJob);
if(Ok == result) {
pCtrl->pFlushLock->lock();
if(true == getFlushBlockStatus(pCtrl)) {
pCtrl->pFlushOK->wait(pCtrl->pFlushLock->getNativeHandle());
}
pCtrl->pFlushLock->unlock();
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to trigger" << endl;
}
if(true == forceFlush) {
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->lock();
setFlushStatus(hJob, Noflush);
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->unlock();
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
|
反注册工作线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| Result ThreadManager::unregisterJobFamily(JobFunc jobFuncAddr, const char* pJobFuncName,
JobHandle hJob)
{
Result result = -EFailed;
RegisteredJob* pRegisteredJob = NULL;
m_pRegisteredJobLock->lock();
pRegisteredJob = getJobByHandle(hJob);
if(true != isJobAlreadyRegistered(&hJob)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to unregister job " << pJobFuncName << " FuncAddr " <<
jobFuncAddr << " result " << result << endl;;
} else if(NULL != pRegisteredJob) {
uint32_t slot = pRegisteredJob->slot;
result = stopThreads(hJob);
if(Ok == result) {
m_threadWorker[slot].data.pq.clear();
m_threadWorker[slot].data.pq.shrink_to_fit();
::memset(&m_registeredJobs[slot], 0x00, sizeof(RegisteredJob));
m_threadWorker[slot].threadId = 0;
m_threadWorker[slot].workThreadFunc = NULL;
m_threadWorker[slot].pContext = NULL;
::memset(&m_threadWorker[slot].ctrl, 0x00, sizeof(ThreadControl));
m_threadWorker[slot].isUsed = false;
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to stop thread" << endl;
}
}
m_pRegisteredJobLock->unlock();
return result;
}
Result ThreadManager::stopThreads(JobHandle hJob)
{
Result result = Ok;
ThreadConfig* pCfg = getThreadConfigByHandle(hJob);
ThreadData* pData = getThreadDataByHandle(hJob);
ThreadControl* pCtrl = getThreadControlByHandle(hJob);
if((NULL == pCfg) || (NULL == pData) || (NULL == pCtrl)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to get threadconfig/threaddata/threadcontrol" << endl;
result = -EFailed;
} else {
result = flushJob(hJob, false);
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->lock();
setFlushStatus(hJob, Noflush);
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->unlock();
pCtrl->pThreadLock->lock();
setStatus(pCtrl, Stopped);
pCtrl->pReadOK->signal();
pCtrl->pThreadLock->unlock();
OsUtils::threadTerminate(pCfg->hWorkThread);
pCtrl->pReadOK->destroy();
pCtrl->pReadOK = NULL;
pCtrl->pThreadLock->destroy();
pCtrl->pThreadLock = NULL;
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock->destroy();
pCtrl->pFlushJobSubmitLock = NULL;
pCtrl->pQueueLock->destroy();
pCtrl->pQueueLock = NULL;
pCtrl->pFlushLock->destroy();
pCtrl->pFlushLock = NULL;
pCtrl->pFlushOK->destroy();
pCtrl->pFlushLock = NULL;
}
return result;
}
|
总结
其实可以看到,设计一个线程池的逻辑不是很复杂,只要理清楚里面的一些线程状态,已经确保他们的状态被锁保护,这里面针对于每一个线程主体,只用到了2个条件信号量来保证一个线程的创建和销毁。
下面是一段简单的使用代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| ThreadManager* threadManager;
static void* testJobFunc(void* ptr)
{
StopWatch stopWatch("job");
int32_t elapsedMillis = ns2ms(stopWatch.elapsedTime());
LOG(INFO) << "ElapsedMillis: " << elapsedMillis << endl;
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
google::InstallFailureSignalHandler();
google::InstallFailureWriter(&signalHandle);
ThreadManager::create(&threadManager, "TestThreadManager");
for(int i = 0; i < TEST_MAX_COUNT; i ++) {
jobs[i] = InvalidJobHandle;
threadManager->registerJobFamily(testJobFunc, "testJobFunc", &jobs[i]);
string serviceName = StringUtils::stringFormat("service-%04d", i);
services[i] = hub->getService(serviceName.c_str());
}
****for(int i = 0; i < TEST_MAX_COUNT; i ++) {
counts[i] = i;
threadManager->postJob(jobs[i], &counts[i], 0);
}
return 0;
}
|