bazel构建C++工程
1. bazel介绍
Bazel是一个开源的构建和测试工具,类似于Make、Maven和Gradel。Bazel支持多种语言的项目,并未多种平台构建输出。Bazel支持跨多个存储库和大量用户的大型代码库。
2. bazel安装
bazel安装有两种方法,一种是通过安装,另一个是通过下载安装包本地安装。ubuntu系统建议使用第一种安装方式。
第一步:添加bazel分发url作为包源
1 | sudo apt install curl gnupg |
第二步:安装或者更新bazel
1 | sudo apt update && sudo apt install bazel |
如果已经安装了bazel,需要升级到最新版本的bazel
1 | sudo apt update && sudo apt full-upgrade |
安装特定版本的bazel,例如安装bazel-1.0.0
1 | sudo apt install bazel-1.0.0 |
3. bazel构建工程
bazel里面有构建C++工程的例子,可以通过命令git clone [https://github.com/bazelbuild/examples](https://github.com/bazelbuild/examples)下载,需要的代码位于example/cpp-tutorial目录中,目录结构如下:
1 | cpp-tutorial/ |
下面对这个C++工程进行解析。
3.1 设置工作区
在构建项目之前,需要设置项目工作区,这个工作区就是一个包含项目源文件的目录和bazel构建输出,bazel识别WORKSPACE和BUILD这两个文件。
- WORKSPACE文件将目录及其内容识别为Bazel工作区,位于项目目录结构的根目录中
- BUILD文件会有一个或者多个,分别构建项目的不同部分
3.2 理解BUILD文件
BUILD文件包含Bazel的几种不同类型的指令,最重要的啥类型是构建规则,它告诉bazel如何构建所需的输出,比如可执行的二进制文件或者动态/静态库。构建文件中构建规则的每个实例称为目标,并指向一组特定的源文件和依赖项。一个目标也可以指向其它目标。
看一下cpp-tutorial/stage1/main中BUILD文件:
1 | cc_binary( |
在示例中,hello-world目标实例化了bazel的内置cc_binary规则。规则告诉bazel建立一个独立的可执行二进制hello-world.cc源文件没有依赖性。
3.3 使用bazel编译项目
构建示例项目,切换到cpp-tutorial/stage1目录,运行以下命令:
1 | bazel build //main:hello-world |
注意目标标签 —— //main:部分是构建文件相当于工作区根的位置,helllo-world是我们在构建文件中命名的目标。
1 | bazel build //main:hello-world |
测试输出如下:
1 | ./bazel-bin/main/hello-world |
3.4 查看依赖图
成功的构建将在构建文件中现实的生命其所有依赖项。Bazel使用这些语句创建项目的依赖关系图,从而实现精确的增量构建。将示例项目的依赖关系可视化。首先,生成依赖关系图的文本表示:
1 | bazel query --notool_deps --noimplicit_deps "deps(//main:hello-world)" \ |
上面的命令告诉bazel寻找target //main:hello-world的所有依赖项,并将输出格式化为图形,然后可以使用GraphViz查看。
可以通过管道直接输出到xdot来生成和查看图形:
1 | sudo apt update && sudo apt install graphviz xdot |
生成图形:
1 | xdot <(bazel query --notool_deps --noimplicit_deps "deps(//main:hello-world)" \ |
依赖图如下:
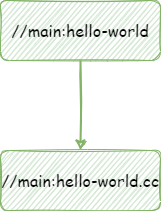
3.5 多个目标文件(target)编译
将示例项目构建分成两个目标。看一下cpp-tutorial/stage2/主目录中的构建文件:
1 | cc_library( |
对于这个构建文件,bazel首先构建hello-greet库(使用bazel内置的cc_library规则),然后构建hello-world二进制文件。hello-world目标中deps属性告诉bazel需要hello-greet库来构建hello-world二进制文件。
切换到cpp-tutorial/stage2目录。运行:
1 | bazel build //main:hello-world |
依赖关系如下:
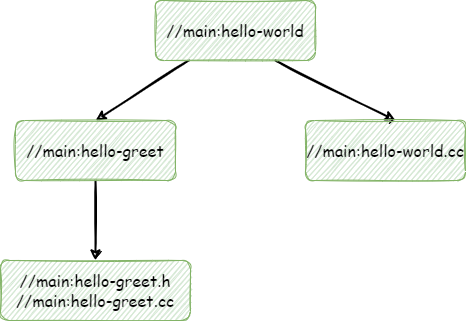
3.6 多个项目包(packages)编译
将项目分离成多个包,看一下cpp-tutorial/stage3目录的内容:
1 | |-- README.md |
现在有两个子目录,每个子目录都包含一个BUILD文件。因此,对于bazel来说,工作空间现在包含两个包,lib和main,先看一下lib/BUILD文件
1 | load("@rules_cc//cc:defs.bzl", "cc_library") |
还有main/BUILD文件:
1 | load("@rules_cc//cc:defs.bzl", "cc_binary", "cc_library") |
主包中的hello-world目标依赖于lib包中的hello-time目标(因此是目标标签//lib:hello-time)——bazel通过deps属性知道这一点。依赖关系:
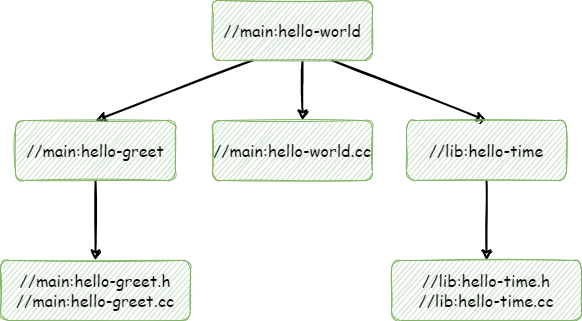
注意,为了使构建成功,使用visibility属性使得lib/BUILD中的//lib:hello-time目标对于main/BUILD中的目标显示可见。这是因为默认情况下,目标只对同一构建文件中的其它目标可见。(Bazel使用目标可见性来防止诸如库中包含的实现细节泄漏到公共API等问题)
编译和运行和上面一致:
1 | bazel build //main:hello-world |




