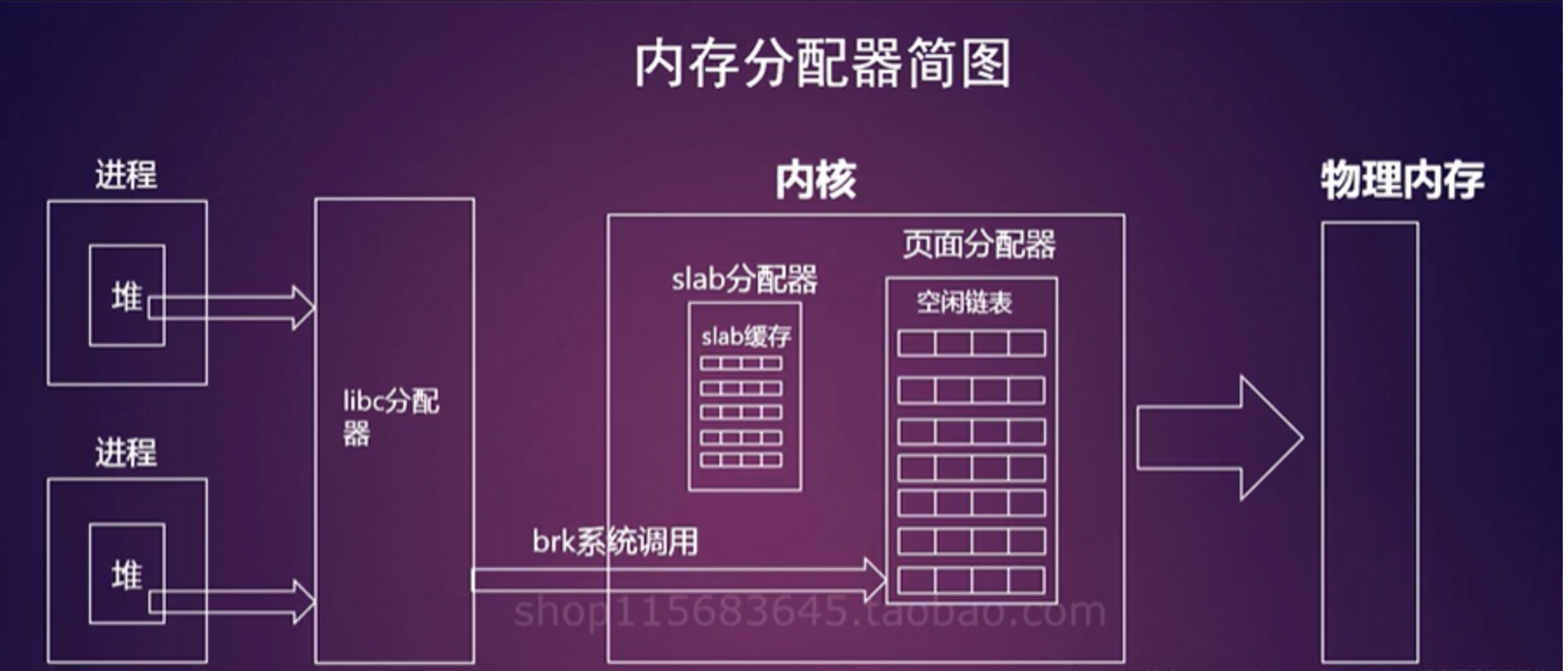
我的内存呢?Linux MemAvailable 如何计算
使用Linux开发是常见的问题是:我的内存呢?怎么只剩这么点了?这是怎么回事呢?
消失的内存
通常我们会用free命令(如下)或Node Exporter + Prometheus 来监控系统的内存。
1 | # free |
上面的输出中,我们很自然的以为free代表可用内存,所以经常会发现这个值特别低,造成“系统的内存用光”的错觉。在比较新的内核里,会有available一项,它才是“可用内存”。
这里有个小知识,free指的是完全没有被用到的内存,而Linux认为内存不用也是浪费,因此会尽量“多”地把内存用来做各种缓存,提高系统的性能。在内存不够用时,它会释放缓存腾出空间给应用程序。因此早期没有available这项指标时,一般会认为free + buff/cache是系统当前的可用内存。那么现在的available是如何计算得到的?
MemAvailable估算
free命令只输出简单几项指标,更详细的指标可以用cat /proc/meminfo得到:
1 | MemTotal: 32729276 kB |
指标非常多,一般需要对内核有一定了解才能看懂。这些指标的基础上,有:
1 | MemAvailable <= MemFree + Active(file) + Inactive(file) + SReclaimable |
要理解这个公式,需要了解Linux是如何管理内存的。Linux对内存的管理有多种视角。
- 系统内存 = 空闲内存 + 内核内存 + 用户内存
- 内核内存 = Slab + VmallocUsed + PageTables + KernelStack + HardwareCorruped + Bounce + X
- Slab = SUnreclaim + SReclaimable,其中
SReclaimable指可回收部分
- Slab = SUnreclaim + SReclaimable,其中
- 用户内存有两个视角:
- LRU视角 = Active + Inactive + Unevictable + (HugePages_Total * Hugepagesize)
- Active与Inactive内存指的是活跃程度,如果内存紧张,会优先释放Inactive的内存
- Active = Active(File) + Inactive(Anon)
- Inactive = Inactive(File) + Inactive(Anon)
- File-Backend内存会与磁盘中的文件关联,于是如果内存不足时可以先写回磁盘释放内存;Anonymous内存不与文件关联,因此除非有swap文件,否则无法释放
- 缓存视角 = Cached + AnonPages + Buffers + (HugePages_Total * Hugepagesize)
- LRU视角 = Active + Inactive + Unevictable + (HugePages_Total * Hugepagesize)
综合上述信息,可以看到可以释放的部分有:
- Slab的
SReclaimable,是内核可释放的部分 - 所有的File-Backend内存 = Active(File) + Inactive(File)
MemAvailable公式的由来就很自然而然了。等等!?公式里的符号为什么是小于等于,不是等于?
详细逻辑与样例
上面的公式在详细计算时,并没有考虑watermark(虽然代码里有),并且最新的内核已经修改了计算公式,考虑了更多的内容。
- 计算
wmark_low。low watermark,当系统可用内存小于low watermark时,kswapd进程会开始尝试释放内存页。首先收集需要的信息:每个ZONE都有自己的low watermark(单位为页,页大小为4K),计算如下1
2
3
4# cat /proc/zoneinfo | grep min
min 1
min 184
min 167101
2wmark_low = (1 + 230 + 20887) * 4
= 84472 (KB) - 计算空闲页
free_pages,可以直接由/proc/zoneinfo中获取:加总即得到1
2
3
4# cat /proc/zoneinfo |grep 'free '
nr_free_pages 3969
nr_free_pages 611300
nr_free_pages 59976587free_pages:1
2free_pages = (3969 + 611300 + 59976587) * 4
= 242367424 (KB) - 计算保留内存。保留内存需要综合考虑各项指标:
lowmem_reserve_ratioZONE是逻辑上的划分,lowmem是指低位的ZONE为高位ZONE预留的内存。每个ZONE都会为高位的ZONE做预留,因此结果是个矩阵:1
2
3
4# cat /proc/zoneinfo | grep 'protection'
protection: (0, 2815, 257771, 257771)
protection: (0, 0, 254955, 254955)
protection: (0, 0, 0, 0)- high watermark。高水位线,可用内存超出时,
kswapd会暂停工作。1
2
3
4# cat /proc/zoneinfo | grep 'high '
high 1
high 276
high 25065 - managed内存,没查到出处,大概指可被使用的内存。
1
2
3
4# cat /proc/zoneinfo | grep 'managed'
managed 3977
managed 720847
managed 65268660 - 计算如下:
total_reserved = Σ(min((max(lowmem) + high_watermark), managed))1
2
3
4
5
6
7total_reserved = Σ(min((max(lowmem) + high_watermark), managed))
= min(max(0, 2815, 257771, 257771) + 1, 3977)
+ min(max(0, 0, 254955, 254955) + 276, 720847)
+ min(max(0, 0, 0, 0) + 25065, 65268660)
= 3977 + 255231 + 25065
= 284273 (page)
= 1137092 (kB)
- 计算
pagecache = active file + inactive file,File Backend 的内存可以被释放。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8# cat /proc/zoneinfo |grep nr_active_file
nr_active_file 0
nr_active_file 6032
nr_active_file 168031
# cat /proc/zoneinfo | grep nr_inactive_file
nr_inactive_file 0
nr_inactive_file 1833
nr_inactive_file 500641
2
3
4pagecache = active file + inactive file
= (0 + 6032 + 168031) + (0 + 1833 + 50064)
= 225960 (page)
= 903840 (kB) pagecache -= min(pagecache / 2, wmark_low),并不是所有的 pagecache 都被认为是可用的:1
2
3
4
5pagecache -= min(pagecache / 2, wmark_low)
-= min(903840/2, 84472)
-= 84472
= 903840 - 84472
= 819368 (KB)- 计算
SReclaimable1
2
3
4# cat /proc/zoneinfo | grep nr_slab_reclaimable
nr_slab_reclaimable 0
nr_slab_reclaimable 428
nr_slab_reclaimable 369891
2SReclaimable = (0 + 428 + 36989) * 4
= 149668 (kB) SReclaimable -= min(SReclaimable/2, wmark_low),和 pagecache 相似,不能全用。1
2
3
4
5SReclaimable -= min(SReclaimable/2, wmark_low)
-= min(149668 / 2, 84472)
-= 74834
= 149668 - 74834
= 74834 (kB)available = free_pages - total_reserved + pagecache + SReclaimable最终的结果与1
2available = 242367424 - 1137092 + 819368 + 74834
= 242124534 (kB)/proc/meminfo的输出(和上小节的数据不同)只有细微的区别:实际上差了约 13MB 左右,不过 zoneinfo 和 meminfo 的输出中间有少许的时间间隔,不确定是不是中间内存有了变化。****1
2
3
4
5
6# cat /proc/meminfo
MemFree: 242385648 kB
MemAvailable: 242137968 kB
Active(file): 689852 kB
Inactive(file): 209196 kB
SReclaimable: 149668 kB
补充:进程内存
知道了系统级别的统计方法,自然会想和进程级别的统计做个对应关系。虽然有不少统计进程内存使用的方法,
但基本上没办法精确地和系统统计对应。进程的统计指标一般有这几个:
VSZ:虚拟内存,不直接对应到物理内存RSS:常驻内存,可以理解成映射的内存的总和。注意进程间有共享的内存页(如 libc 库),不同进程加总时会重复计算这部分PSS:与RSS几乎相同,区别在计算时进程共享的内存时,除于了共享的进程数量,因此可以用来加总USS:该进程独立占用的内存,即扣除了共享的内存页
VSZ 和 RSS 可以直接通过 ps aux 输出:
1 | $ ps aux|head |
PSS 和 USS 可以通过 /proc/<pid>/smaps 中的字段统计得到。也可以用工具 smem 直接输出和统计。
1 | # PSS:通过 Pss 字段相加得到 |
小结
介绍了几个知识点:
free中的available才是可用内存/剩余内存MemAvailable <= MemFree + Active(file) + Inactive(file) + SReclaimable- MemAvailable 具体的计算方式,涉及到 ZONE, lowmem, watermark 等知识
- 补充了进程内存的一些统计方式(RSS、PSS、USS)
好吧,对写业务的我其实也没什么用。
参考
- https://access.redhat.com/solutions/22177 RedHat 对
/proc/meminfo的解释 - Analyzing Memory Usage in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 对进程内存和物理内存映射关系的讲解
- LINUX MEMORY EXPLAINED 对进程的 VSZ、RSS、PSS、USS 有详细讲解
- /PROC/MEMINFO之谜 讲解了 meminfo 中一些“加起来不刚好”的项的原理
- https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/proc.5.html
/proc/smaps文件格式 - https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/vm/pagemap.txt
/proc/pagemap文件格式,内容上可以理解为是 smaps 的数据来源